Neural Network: Supervised Learning
Wed, 12 Jun 2024, by Yash Sharma
Introduction to neural network and supervised learning, underlying concepts and mathematics.
What is a Neural Network ?
Neural networks are inspired by the structure and function of the human brain. They consist of interconnected nodes as neurons and they are arranged in layers and the layers are interconnected. Each node holds some value and the connections holds some weight.
The simplest neural network would be, when a node (input node) is connected with another node (output node).
where, is called input node and is called output node, and they are connected through a weight . To get the output we just need to multiply the value of input node to the weight
Now, Let see a neural network with more nodes and connections:
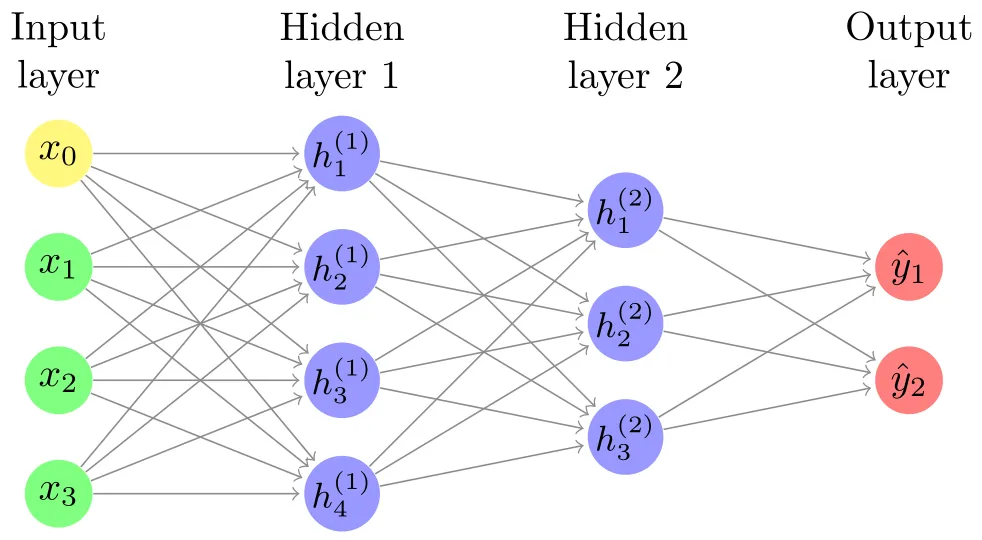 Here we can see there are nodes are connected with multiple nodes through multiple weights.
We call each column of nodes, a layer. First layer is input layer, last one is output layer and the layers in between are called hidden layers. We give input to the neural network through input layer then it does some fancy calculations (we will come to that soon) and give us output in output layer.
Here we can see there are nodes are connected with multiple nodes through multiple weights.
We call each column of nodes, a layer. First layer is input layer, last one is output layer and the layers in between are called hidden layers. We give input to the neural network through input layer then it does some fancy calculations (we will come to that soon) and give us output in output layer.
How Neural Network Learns?
You will wonder how these connected nodes learns to do tasks. The weights of the connections plays the main role in learning of the neural network. Weights are fined tuned so that the neural network do some specific task for us.
There are three ways it can learn:
- Supervised Learning
- Unsupervised Learning
- Reinforcement Learning
Here we are going to discuss about Supervised Learning.
Supervised Learning:
We know that for any neural network it takes N input values and generate M outputs by propagating through the hidden layers, this is called Forward Propagation. The MAIN learning occurs when we take the output and compare it to the desired output and then tweak the weights so that it gives us the desired output, this is called Backward Propagation or Error Correction.
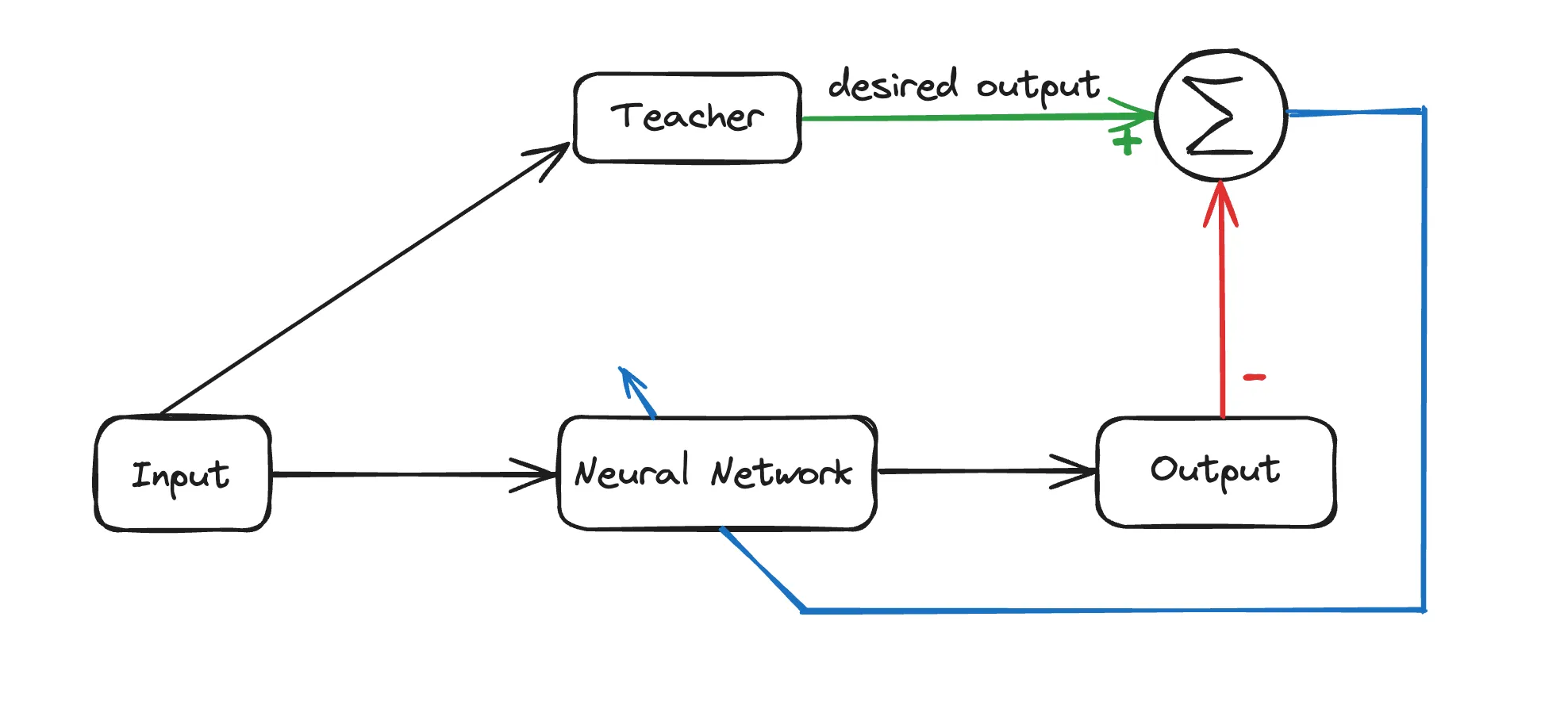
Let’s take a example:
Suppose you have an untrained neural network that recognise handwritten digits and you chose supervised learning to train the neural network. So its training process is as follows:
-
Feeding the Network: Imagine showing the neural network a picture of a handwritten digit, like a 3. This image gets converted into a format the network can understand, like a series of numbers representing brightness levels.
-
Making a Guess (Forward Propagation): The network processes the information and makes an initial guess about what digit it’s seeing. It might guess a 5 or a 7.
-
Checking the Answer Key: We have the correct answer (the 3) from the MNIST dataset. We compare the network’s guess to the actual digit. We subtract the desired output from the output column vector and calculate the error . For the given example .
-
Learning from Mistakes: If the guess was wrong, we calculate the difference between the network’s output and the correct answer. This difference tells us how far off the guess was. We calculate the error and add the square of each error (to make them +ve) to get the cost function.
-
Fine-Tuning (Gradient Descent): Like a student learning from corrections, the network adjusts the connections between its internal processing units (weights) based on the error.
These adjustments are tiny, but over many training examples, they help the network make better guesses in the future.
Maths behind the Neural Network
Now is the time to learn the mathematics behind this all.
Neural networks use a lot of math under the hood, but you don’t need to understand all of it to use them effectively. Here’s a high-level look:
- Linear Algebra: At its core, neural networks uses matrices and vectors, and perform linear math operations like addition, multiplication, and vector dot products. These operations combine the inputs with weights to arrive at an intermediate value.
- Activation functions: These functions introduce non-linearity into the network. They take the intermediate value and transform it into the output. This allows the network to learn complex patterns.
- Calculus: Backpropagation, a core training algorithm, relies on calculus to efficiently adjust the weights based on the errors between the network’s output and the desired output.
To generate the output it uses Linear Algebra:
where : next layer,
: current layer,
: weights connecting and ,
: baises (the are used to add some offset to the values)
: activation function (eg: ReLU = , = etc.)
Cost Function:
Gradient descent
It is an iterative algorithm commonly used in machine learning to find the minimum of a function. It works by repeatedly adjusting the parameters of the function in the direction that leads the most improvement (like going downhill).
Analogy : Imagine you’re lost in a foggy mountain range and want to find the lowest valley. Gradient descent would be like taking small steps downhill each time, eventually reaching the lowest point.
In machine learning, the cost function represents how well a model is performing, and the parameters are the adjustable settings of the model. By following the gradient descent algorithm, the model can adjust its internal settings to improve its performance on a specific task. Gradient descent uses the idea of derivatives from calculus. In simpler terms, a derivative tells you how steep a graph is at a certain point. It uses the information from the derivative to adjust the model’s settings and improve its performance.
PROCESS: The function to be minimised. The gradient is a vector of partial derivatives indicating the direction of steepest ascent. Parameters are updated as , where is the learning rate. Gradient:
The process is repeated iteratively until convergence, i.e., until the changes in the function value become smaller than a pre-defined threshold, or after a fixed number of iterations.
While calculus is involved behind the scenes, you don’t necessarily need to understand the complex math to use gradient descent effectively in machine learning tools. Many libraries and frameworks handle the underlying calculations for you.
I hope you understood the what is neural network, how it works, and underlying concepts. If you have any feedback, you can email me it will help me improve my content. Thank you!!