Mon, 11 Mar 2024
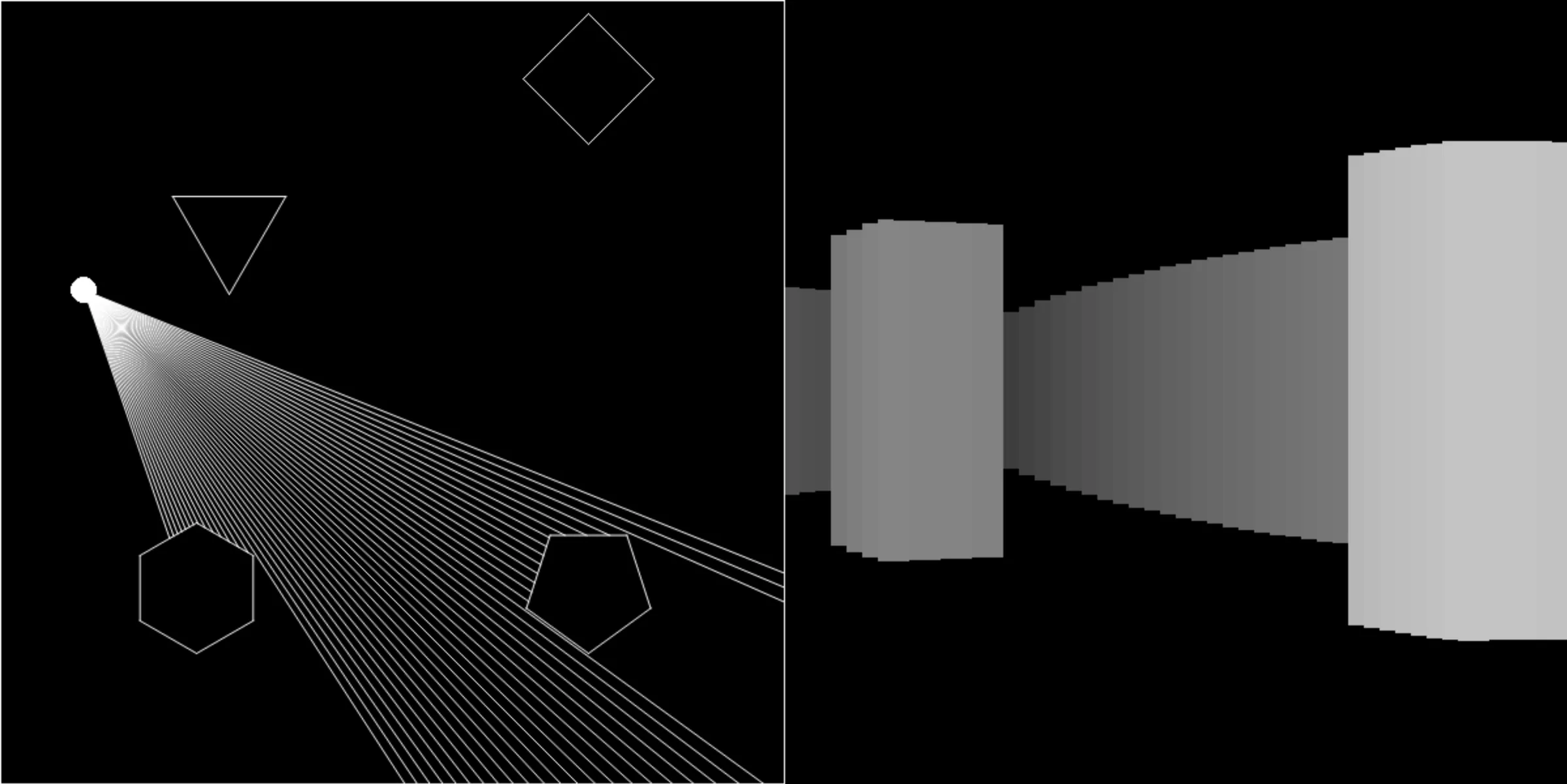
It is a Ray Casting algorithm. In this particle cast rays in its surrounding and an algorithm draw the environment around it.
Introduction
This project implements a Ray Casting algorithm where particles cast rays in their surroundings, and an algorithm draws the environment around them. Ray Casting is commonly used in computer graphics to simulate the way light interacts with objects in a scene. Ray Casting is a technique used to render a 3D scene onto a 2D screen. It involves casting rays from a viewer (camera) into the scene, determining the intersections with objects, and using this information to create a 2D representation of the 3D environment.
Algorithm
The algorithm utilizes three main steps:
- Particle Emission: The particle emits rays into its surrounding environment.
- Ray Intersection Detection: The algorithm checks for intersections between the emitted rays and objects in the surrounding environment.
- Rectangle Drawing: Based on the distance between the camera and the intersection points, the algorithm draws rectangles with corresponding heights and colors. (This process follows the Inverse Square Law.)
Intersection Between two lines
In order to find the position of the intersection in respect to the line segments, we can define lines L1 and L2 in terms of first degree Bézier parameters:
where t and u are real numbers:
the point of intersection:
There will be an intersection if and . The intersection point falls within the first line segment if , and it falls within the second line segment if .
How camera cast rays:
def cast(self, wall: Boundary):
x1 = wall.a.x; y1 = wall.a.y
x2 = wall.b.x; y2 = wall.b.y
x3 = self.pos.x; y3 = self.pos.y
x4 = self.pos.x + self.dir.x; y4 = self.pos.y + self.dir.y
den = (x1 - x2) * (y3 - y4) - (y1 - y2) * (x3 - x4)
if den == 0:
return None
else:
t = ((x1 - x3) * (y3 - y4) - (y1 - y3) * (x3 - x4)) / den
u = -((x1 - x2) * (y1 - y3) - (y1 - y2) * (x1 - x3)) / den
if t >= 0 and t <= 1 and u >= 0:
pt = Vector2D((x1 + t * (x2 - x1)), (y1 + t * (y2 - y1)))
return pt
else:
return NoneInverse Square Law
The Inverse Square Law of light states that the intensity of light or other radiative energy from a point source is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source. Mathematically, it can be expressed as: or more specifically,
where: P: Power of the light source, I: Intensity of the light source, d: Distance from the light source.
Getting Started
Clone the repository and navigate to the project:
git clone https://github.com/Yash2402/Ray-Casting.git
cd Ray-CastingInstall dependencies:
pip3 install -r requirement.txtRun:
python3 main.pyUsage
Learn how to use the Ray Casting algorithm in your project. Configure and run the code using:
- To move the particle use mouse
- To Rotate the FOV Clockwise press
d - To Rotate the FOV Counter-Clockwise press
a